To start this issue I would like to draw your attention to an otherwise marginal article, if it weren't for the conclusions it draws.
Looking at how Nobel prize winners were drawn into declaring their support for genetically modified organisms the oneworld (Nov. 7) article's author comes to some revealing disclosures.
Though this saga has been highlighted earlier on this site, let's start with part of the article's intro:
'In June this year it hit the newspaper headlines. More than a hundred
Nobel laureates call upon Greenpeace to immediately cease their
resistance to genetic modification (GM). In specific the environmental
organization was blasted for it's campaign against so-called “Golden
Rice”, a genetically engineered rice variety
...
Regulatory barriers for GM-technology should therefore be eased, the
letter urges, and calls on “governments of the world“ to make this
happen'.
The
article reveals
- That Greenpeace does not "frustrate" the work of IRRI on Golden Rice,
- that Greenpeace were not allowed to defend themselves at a press conference in Washington D.C., being refused entry by a representative of a PR firm who was formerly head of Monsanto's corporate communication,
- the same person also provided public affairs guidance to the Nobel winners,
- the same representative is a fixer between industry and scientists which seek to discredit organic food industry,
- with this in mind there is apparently a target list of well-known / influential GMO doubters,
- that the leader of Nobel Laureates efforts in this cause has a private stake in allowing wider acceptance of GMO's.
It just proves to what lengths corporations are willing to go to reap higher returns where whatever the truth may be is lost. Here one sees how a simple rice related issue is part of a strategy to avoid questions and possible consequences, all for a greater greed. A lot has been said about the ability of internet to withhold truth and act as an echo chamber. Blatantly shouter louder than those who seek a more balanced picture seems to be all the rage.
The Guardian (Nov. 30) has a similar article but then on the bigger picture.
Cambodia
Main news from Cambodia is it's unsuccessful bid to become World's Best Rice; apparently the competition has decided not to be upstaged by Cambodia. The Phnom Penh Post (Nov. 21):
'Cambodia's Phka Rumdoul variety of fragrant rice, which won the World’s
Best Rice award for three consecutive years from 2012 to 2014, narrowly
missed its fourth crown at this year’s awards held in Chiang Mai in
northern Thailand last week'.
Other news from the Kingdom's rice scene. Main point is of course the decreasing price for the fresh harvest.
Solving problems the Khmer way. CNV.org (Nov. 22):
'To prevent the falling rice prices, Samdech Techo Hun Sen called on the
farmers to keep and dry up their rice yields well, and sought
understanding from the microfinance institutions that have provided
loans to farmers, stressing that not only Cambodia, but other countries
in the region and the world have been facing with this low rice prices'.
The VoA (Nov. 24) worded roughly the same:
'Prime Minister Hun Sen on Monday urged Cambodian farmers to put off
sales of rice due to recent falls in the commodity’s price on
international markets'.
Well, I doubt this will have any effect, bills need to be paid and who says that prices will rise in the (near) future?
Sectoral news, one wold say in the same vein. The Phnom Penh Post (Nov. 25):
'It has been over two months since the government made available
a $27 million emergency loan package to the beleaguered rice sector,
yet only 5 percent of the funds have been disbursed.
Officials from the state-owned bank in charge of issuing the loans claim
the low figure is proof that rice millers’ claims of facing imminent
bankruptcy were overblown, while rice industry players charge it is
because the lending comes with onerous strings attached.
...
Yang Phirom, a business advisor for Cambodian Centre for Study and
Development in Agriculture (CEDAC), said that the RDB’s 7 percent annual
interest rate was too high.
“Based on our observations, the interest rate of loan from the RDB is
still high compared to other countries that are offering lower interest
rates,” he said. “Most of the rice millers would not dare to apply for
the government’s loans as they are not confident that they will be able
to pay them back.”
Additionally, he said that the sector was still faced with large
quantities of illicit milled rice coming in from Vietnam, while paddy
rice was going out, skewing Cambodia’s rice prices and its ability to
compete even domestically.
“These challenges still have not been addressed,” Phirom said'.
It sort of underlines how the Khmer government has little power to persuade the market whichever way it's being directed. The growth of Cambodia's export market has been mostly due to higher prices and little competition from Thailand with private companies behind the driving wheel.
In a buyers market with depressing prices, Cambodia's produce is simply not competitive enough with the same private monies opting for better opportunities elsewhere.There's more to note on this issue. The Phnom Penh Post (Dec. 1):
'Frustrated with the failure of a $27 million emergency loan package to
help rice farmers find a fair market price for their crop and stem the
tide of smuggled paddy across the borders, Agriculture Minister Veng
Sokhon is flogging a new model for the nation’s restive rice farmers:
contract rice farming'.
Overall, contract farming has it's merits but with decreasing prices, there's usually little appetite with traders and millers; after all lower prices mean an oversupply in the market which consequently results in millers less eager to purchase harvests, let alone put them in stick; unless they were able to negotiate prices lower or equal to harvest value. On the other hand with prices rising, farmers will feel outdone as they had previously negotiated a price which seemed realistic at the time, but at the time of sale itself they will observe that traders are making an easy profit.
The examples highlighted were all of either limited impact or niche products where prices tend to not follow market prices as much as the mainstream products.
Even more marginal comes this bit of rice news from the Phnom Penh Post (Nov. 7). Tedious at the least:
'The government is seeking funding to complete its effort to draft
standards for 11 local varieties of rice as part of an initiative aimed
at facilitating efforts to market Cambodia’s most important agricultural
crop, a government official said yesterday.
Chheng Uddara, a department director at the Institute of Standards of
Cambodia (ISC), said standards for eight varieties have been drafted
with the financial support of the multi-donor Trade Development Support
Program (TDSP), but the funding only covers about half of the
development process'.
Rhetoric
There's lots to report from Thailand as saving the rice farmers (or at least the notion of saving) has propelled the ingrained instability of rice market to the forefront. Prior apologies for the what has turned out to be a seemingly never ending list of links and quotes ...
Same same. The main problem are prices dropping just before the majority of Thailand's rice harvest.
Though rice prices are very much dependent on the world market, in Thailand much effort is wasted on the blame game.
'Some 30 executive committee members of the Thai Rice Millers
Association have stepped down amid criticism that rice millers are
behind the recent slump in rice prices.
...
Prime Minister Prayut Chan-o-cha earlier blamed rice mill
operators and some local politicians for manipulating rice prices,
causing the price plunge'.
'While the government and farming industry have blamed each other
for the sharp drop in rice prices, a leading economist says the tumbling
prices, particularly for premium fragrant rice, stem from diverse factors'
Solutions to the price drops? The Bangkok Post on November 3:
'Major Thai oil and gas companies have jointly launched
rice-selling programmes to help farmers who are struggling with low rice
prices due to oversupply'.
'People have responded warmly to the farmer-to-consumer rice
markets popping up all over the country, with at least two provinces
reporting brisk sales on the first day'.
Bangkok Post (Nov. 14):
'Almost 300 buyers from 41 countries have been brought together
with sellers of Thai rice and cassava, and their processed products, at a
four-day meeting the Commerce Ministry hopes will generate 63
billion baht in sales'.
'Thai exporters yesterday signed five memorandums of understanding
(MoUs) for a combined 11,000 tonnes of rice and 800,000 tonnes of
tapioca chips with Hong Kong buyers at a business matching event organised by the Commerce Ministry'.
But these of course will never dent the price drop. So the next thing coming up is to cool potential hotheads.
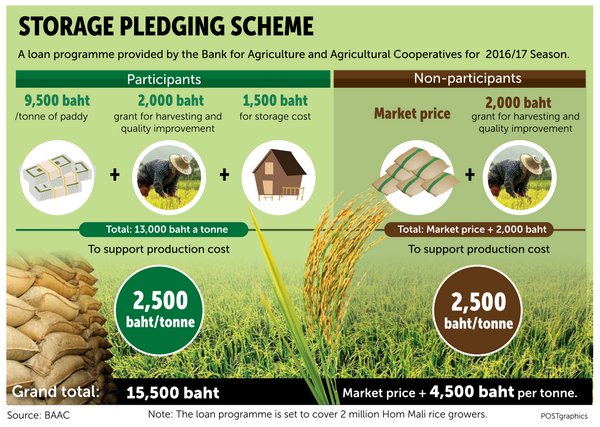
The Bangkok Post on November 4:
'The
government's scheme (above) to delay releasing 10 million tonnes of
new rice supply to the market, aimed at propping up sinking prices, will
use a combined 127 billion baht in loans and subsidies, says the chief
of the Bank of Agriculture and Agricultural Cooperatives (BAAC)'.
Bangkok Post (Nov. 6):
'Prime Minister Prayut Chan-o-cha has called an urgent meeting with the
National Rice Policy Committee to draw up relief measures for rice
farmers before a new supply of grains hits the market this month.
...
A source at the Agriculture and Agricultural Cooperatives Ministry said
the meeting was prompted by the death of a Phichit rice farmer who
allegedly committed suicide due to stress over heavy debts.
...
The spokesman declined to respond to Pheu Thai politicians' criticism of
the government's handling of the rice price fall, saying Gen Prayut
urged restraint to avoid friction and told concerned authorities to
focus on addressing the problems'.
The Bangkok Post on November 8:
'The National Rice Policy Committee agreed on Monday to launch a
new subsidy scheme worth 18 billion baht to aid struggling farmers amid
plunging rice prices'.
But it doesn't seem enough. The Bangkok Post (Nov. 10):
'The
regime's responses to plummeting rice prices have been both
disappointing and disastrous to it and farmers. The worst came from
government spokesman, Lt Gen Sansern
Kaewkamnerd, who said a 43-year-old farmer in Phichit, who committed
suicide because of debt caused by the price crisis, "was not a farmer,
but an air-conditioner mechanic". It was a knee-jerk, unchecked and
heartless response.
...
It
is obvious that Gen Prayut is taking cautious steps in
implementing his subsidy scheme, which is, for many people, a model
copied and pasted from many previous governments, including the Yingluck
Shinawatra administration, and repackaged under a new brand.
...
Amid the crisis, the regime was still critical of Ms Yingluck's
"publicity stunt" of buying rice during meetings with farmers last week.
Gen Prayut urged politicians to "stop exploiting the plight of
farmers for political motives'.
'The free-fall in rice prices has sent an economic and political
jolt across the country, and in the process highlighted how "thinking
small" and modest-scale farming just might hold the key to the
survival of farmers. The depressed rice prices, coupled with a growing demand for
organic farm products, are driving the chemical-free rice sector and
earning these growers more income'.
It's an interesting article which highlights how growing for the masses is past-tense; niche marketing is the future.
The Bangkok Post (Nov. 13) notes:
'Rice farmers have begged the government for help as their
stockpiles, which were not bought last year because of oversupply, are
backing up and leaving no room for this year's looming harvest.
...
Mr Nga urged the government to find ways to help farmers release
their stockpiles so they can free-up space for this year's harvest.
In tambon Muang Leang, 73 of 157 households joined the
storage-pledging scheme for the 2015 harvesting season carried out by the Bank for Agriculture and Agricultural Cooperatives'.
What also highlights on the political importance of saving the rice farmers are the Bangkok Post opinions and editorials such as follows from November 6:
'In the early 1980s, as a post-Vietnam war peace took shape in
Southeast Asia, Thailand made an important decision. To be more correct,
Thailand decided not to decide about rice.
In purely logical terms, a la Mr Spock, it was time to shift the
back-breaking burden of rice growing to poorer neighbours in order to
move the economy along to modern development including advanced
agriculture.
...
The root cause is worldwide overproduction of rice. This is
especially true and especially important in Thailand, the world's
leading rice salesman.
But the government for completely understandable political and
populist reasons wants to ignore the "worldwide" part. If there is a
world glut of rice, there's no way to blame profiteering rice millers
and merchants.
...
For the second time since the coup that sought to extinguish populism
forever, Prime Minister Prayut Chan-o-cha had to reach into the
government's money bags to address serious poverty among farmers.
Like the problem with rubber growers, the premier really has no
choice but a populist programme with two so-familiar aims: bail out the
farmers in the short term and try to control the market in the long.
...
Gen Prayut now is equally confident that if he locks up rice stocks --
new rice, at that -- the artificial shortage will raise prices. His
contradiction, arguably even bigger than the Pheu Thai dichotomy, is
that consumer prices are already high and aren't going lower. Ever. And
if he thinks his soldiers can run rice mills and rice marketing, he's
going to be disappointed, to say the least.
..
Gen Prayut's rice problem has barely started. The ability of the
state-owned Bank of Agriculture and Agricultural Cooperatives to finance
another gigantic handout -- the scheme's estimated cost went from 35
billion to 127 billion baht in three days -- is debatable'.
From November 19:
'The
political bickering over how to help farmers suffering from
low rice prices does not serve any purpose except exacerbating their
hardship.
Without a sincere halt to politicising rice prices, it is the rice
farmers -- the very people everyone agrees deserve assistance -- who are
destined to suffer the most.
...
The
current government can use input from rice farmers and
researchers as well about its plan to introduce crop substitutes in
areas deemed inappropriate for rice farming. Maize, the government's
preferred choice for farmers in 35 central provinces instead of
rice, is widely viewed as impracticable because the crop would not grow
well in areas that used to be paddy fields'.
From November 24:
'With just about one year left in office, Prime Minister Prayut
Chan-o-cha and his government will have to give a high priority to
existing problems in agriculture -- especially the falling price of
rice.
...
A rice crisis always hits the government hard. Most of the measures
introduced to tackle falling rice prices were not sustainable.
...
However, none of these subsidies or cash handouts are long-term
solutions. Farmers should be allowed to take the lead in empowering
themselves'.
The author pleads for more farmer training.
And on November 26:
'When
the government gave rice farmers 13,000 baht per tonne to
shore up the all-time-low paddy prices, Boonsong Martthong and hundreds
of organic rice farmers in Yasothon province just could not care less.
Why should they? Why kowtow to the rice millers who give farmers only
7,000 baht per tonne of paddy or rejoice at the state subsidy scheme at
13,000 baht when they can already get 20,000 baht without a fuss. What's
more, their polished organic rice easily gets 45,000 baht per tonne
from health-conscious buyers.
...
According to Greennet, a non-profit organisation, the organic rice market has increased by 28% this year.
...
Despite
state eulogies for the King, an advocate of organic
farming, successive governments all strongly support chemical farming.
The Agriculture Ministry has practically become the mouthpiece for
agro giants -- and agricultural officials their salesmen. It comes as no
surprise then that Thailand is among the world's top users of farm
chemicals.
According to the Agriculture Ministry, Thailand is importing an average
of 160,000 tonnes of farm chemicals.
...
According to the Agriculture
Ministry, Thailand is importing an
average of 160,000 tonnes of farm chemicals a year, costing the country
about 22 billion baht. In the past five years, the import of toxic farm
substances has increased by 50%
That makes Thailand the world's 5th biggest user of farm chemicals,
according to the World Bank. The country's agricultural land area,
however, ranks 48th in the world only. What's more, about 70 chemical
pesticides
used in Thailand are highly hazardous and not allowed in the West.
The results? Most rivers and reservoirs in the country have become
severely contaminated with toxic substances, which go directly to us
consumers through the food chain.
...
The government is also pushing for farm zoning. "But this top-down
policy won't work," Mr Boonsong insisted. "Farn officials don't know
our localities. They don't have field experience. They don't have field experience. They don't have a support system
either. What they can do expertly is telling us what farm chemicals to
buy."
...
The problem, as always, is the gap between state's rhetoric for
environmentally friendly agriculture and and its actions, the farmer
said wearily'.
Conclusions are that current strategies are once more aimed at influencing the market, though they seem more directed at garnering political support. The Thai political setting has always relied on even votes for the whole country. This has created an elite class which sees it's rule being challenged from urban centers, which have the voices but not the votes. So it's no wonder that whoever is at the helm of the country, political reform based on empowering urbanites, is not a notion to be considered.
Finally to sum up the not so regional rice news section, the Vientiane Times (Nov. 25):
'Lao rice cooperatives have made good progress in terms of their rice
production efforts but marketing and sales deficiencies are still
causing problems for the co-ops'.
Others
Well if rice is not moving what is? The Phnom Penh Post (Nov. 23):
Mangoes should also have been on the radar of South Korea. However the Phnom Penh Post (Nov. 18) reports:
'It has been nearly a year since the government signed a memorandum of understanding
with South Korea that aimed to put Cambodian mangoes on the shelves of
supermarkets in Seoul, yet local producers say there is little sign of
any movement.
According to In Chayvan, president of the Kampong Speu Mango
Association, the potentially lucrative trade agreement signed last
December has stalled on South Korea’s stringent sanitary and
phytosanitary (SPS) regulations, which local producers are unable to
comply with.
...
Chayvan said Cambodian mango growers would be better off focusing their
efforts on securing export contracts for China, and upping shipments to
the Thai and Vietnamese markets. He said these countries have less
stringent SPS regulations, while Thailand and Vietnam are ready to bend
the rules on SPS and certificates of origin when their domestic
production is insufficient to meet demand.
...
Mong Reththy, chairman of the agro-industrial conglomerate Mong
Reththy Group, said his company has already shipped mangoes to Europe
this year, and was looking forward to the possibility of exporting them
to South Korea.
However, he said, the Koreans take food safety very seriously and this has proven a stumbling block.
“We are always looking to export to South Korea, but the issue is
whether or not the government could meet their requirements,” he said'.
'Amid reports that Vietnam’s early harvest of cassava is facing downward
price pressure, Cambodian farmers could be in for a rough season as
local prices are largely dependent on those of the Kingdom’s more
developed neighbour, a ministry official said yesterday.
...
“Our experience with the cassava harvest from last year showed that
most farmers lost money and around 40 percent of cassava producers have
already given up on farming,” she said, adding that last year’s average
selling price of 500 riel per kilo was below the 700-riel breakeven
point.
Heang [Sum Heang, head of the Pailin Cassava Association] added that she replaced 200 hectares of cassava with mango trees after losing $70,000 on the crop last year'.
'The government's move to encourage farmers in 35 central provinces
to grow maize instead of rice by giving them an interest rate subsidy
is impracticable, according to a leading member of the provincial farmers assembly.
...
“Over the past years, farmers had responded positively to
government policies. They have grown maize, Crotalaria juncea [brown
hemp or sunn hemp] or beans, but those crops did not grow well in soil
suited for rice. Corn and beans did not give yields, and farmers suffered losses,’’ he said.
The government should ascertain the views of farmers, or listen to their problems before implementing any policies, the Chai Nat farmers’ leader said'.